Methods
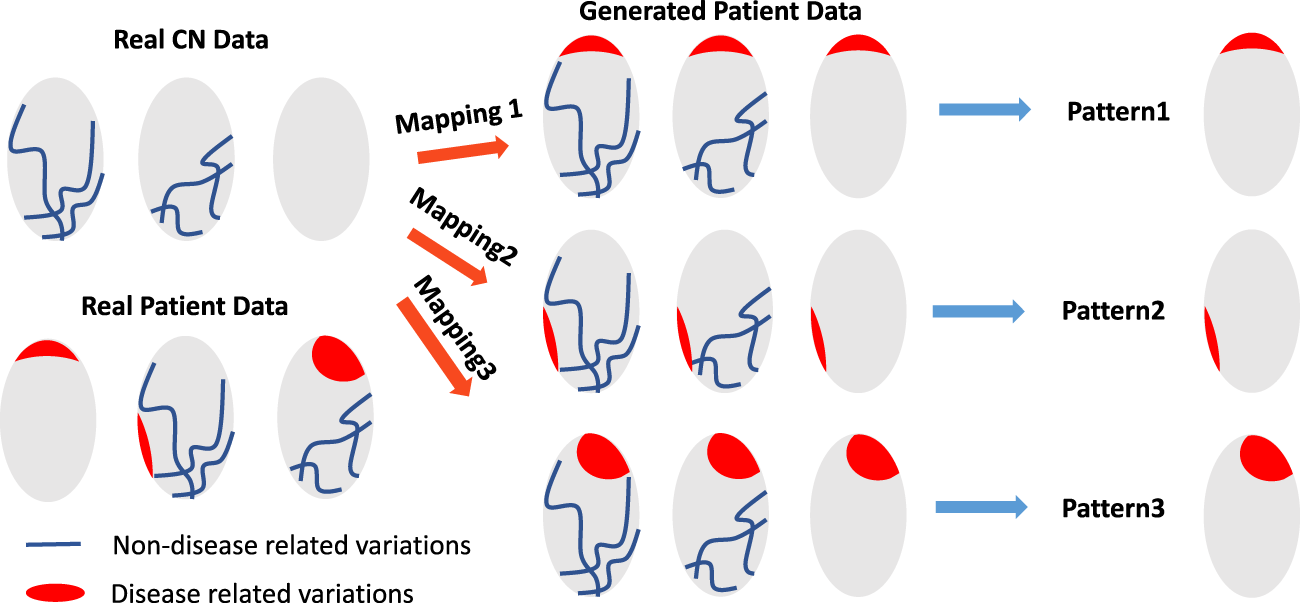
Smile-GAN: Semi-supervised clustering via GAN
Smile-GAN is a semi-supervised clustering method specifically developed to identify disease-related heterogeneity among the patient group. This model successfully eliminates disease-unrelated variations (blue lines) observed in the normal control (CN) group, enabling the clustering of patients based solely on disease-related variations (red regions). Specifically, through joint training of the mapping and clustering function, Smile-GAN finds neuroanatomical pattern types by means of clustering transformations from CN data to patient data.
Publication SoftwareApplications
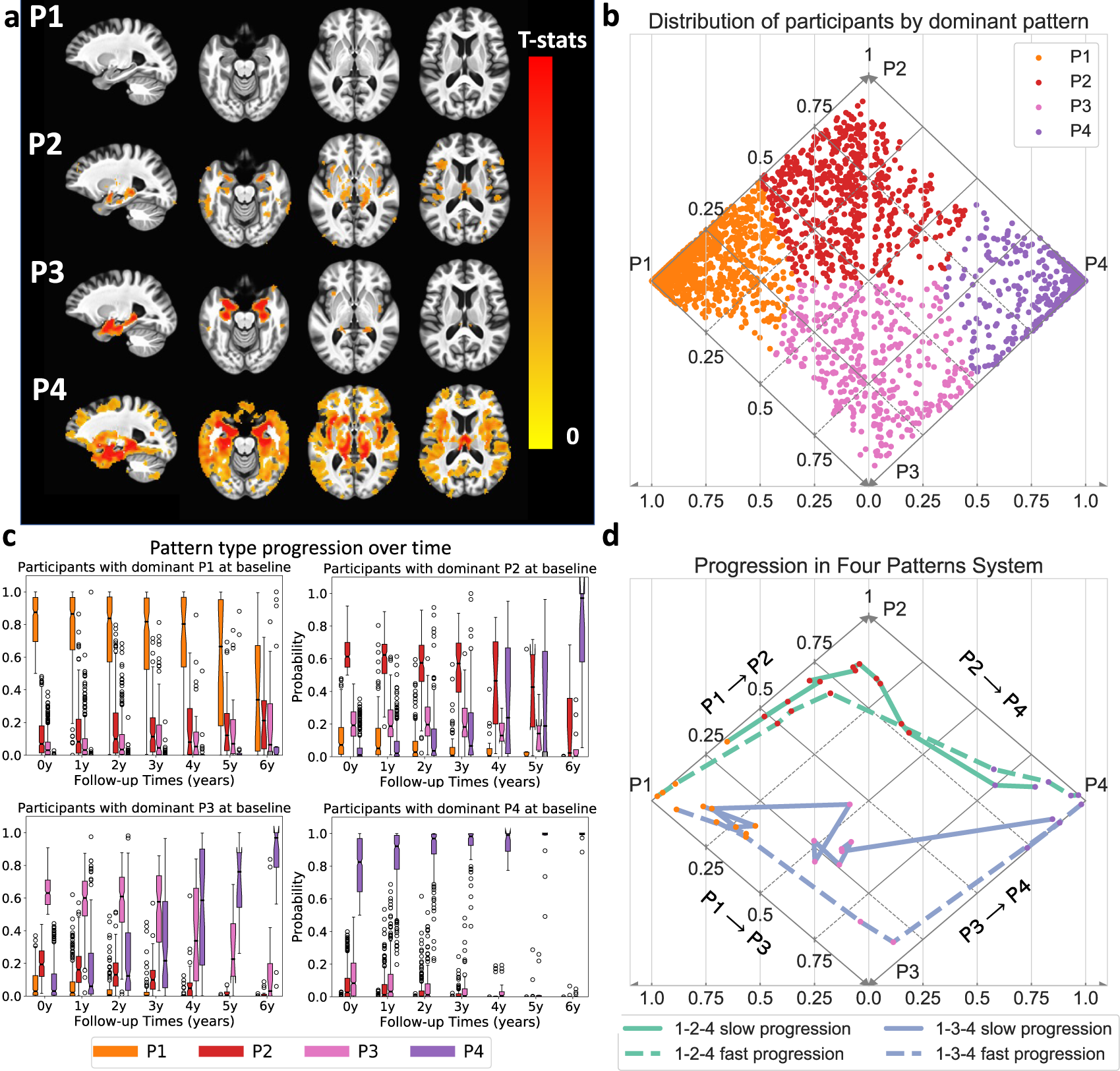
Smile-GAN identifies four pattern types among MCI/AD participants
Smile-GAN identified four patterns types of neurodegeneration related to MCI/Dementia. Applying this framework to longitudinal data revealed two distinct progression pathways. Measures of expression of these pattern types predicted the pathway and rate of future neurodegeneration. Pattern expression offered complementary performance to amyloid/tau in predicting clinical progression. These deep-learning derived biomarkers offer potential for precision diagnostics and targeted clinical trial recruitment. For further details regarding the characteristics of these pattern types, refer to the work of Yang et al.