Methods
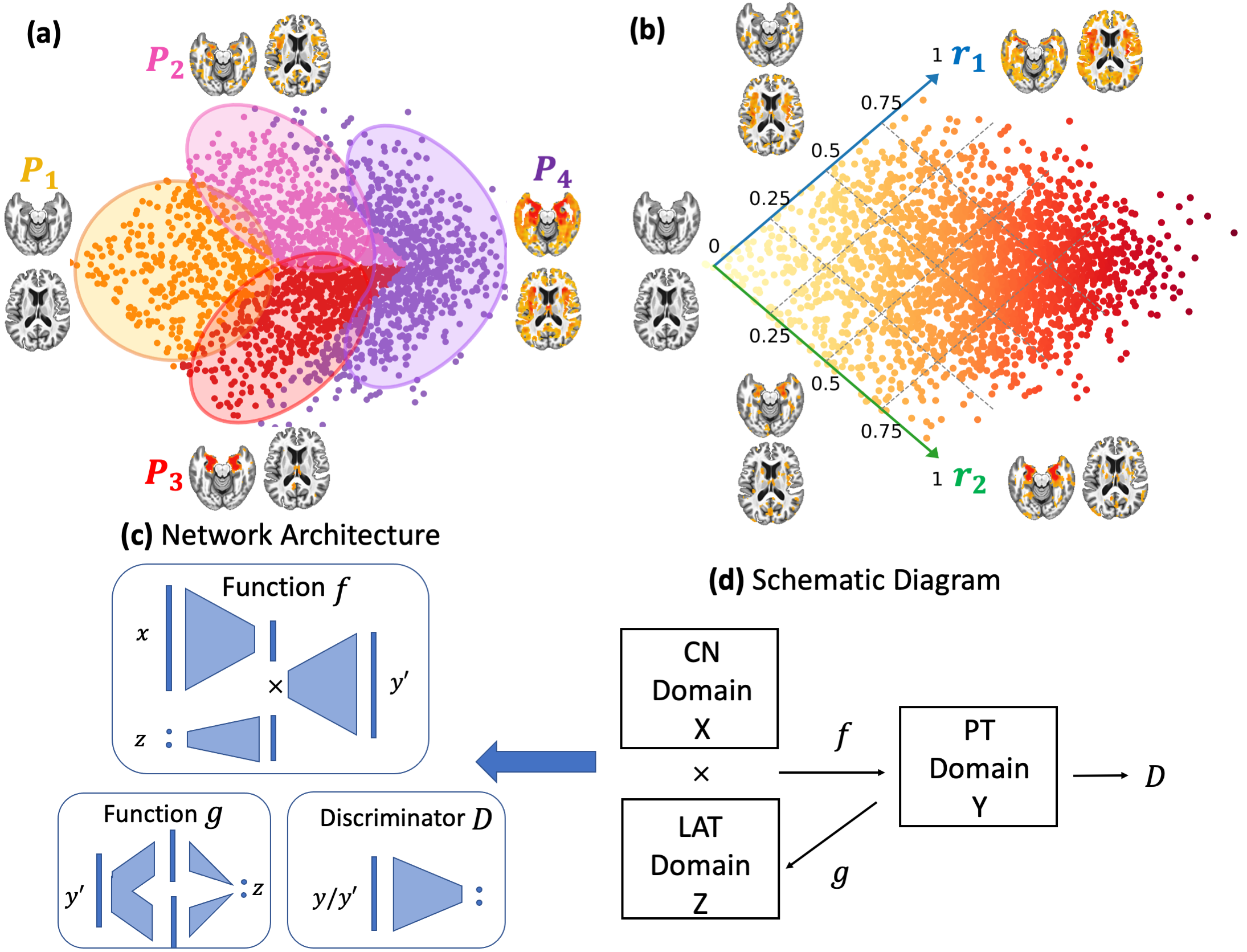
Surreal-GAN: Semi-supervised representation learning via GAN
Surreal-GAN is a semi-supervised representation learning method that is designed to identify disease-related heterogeneity among the patient group. Unlike clustering approaches (e.g., Smile-GAN as shown by (a)), Surreal-GAN proposes a continuously dimensional representation (b) which disentangle brain variations due to disease heterogeneity and severity. Specifically, Surreal-GAN parses complex disease-related imaging patterns into interpretable low-dimensional representation indices (r-indices), with each dimension directly indicating the severity of one relatively homogeneous imaging pattern at individual level.
Publication SoftwareApplications
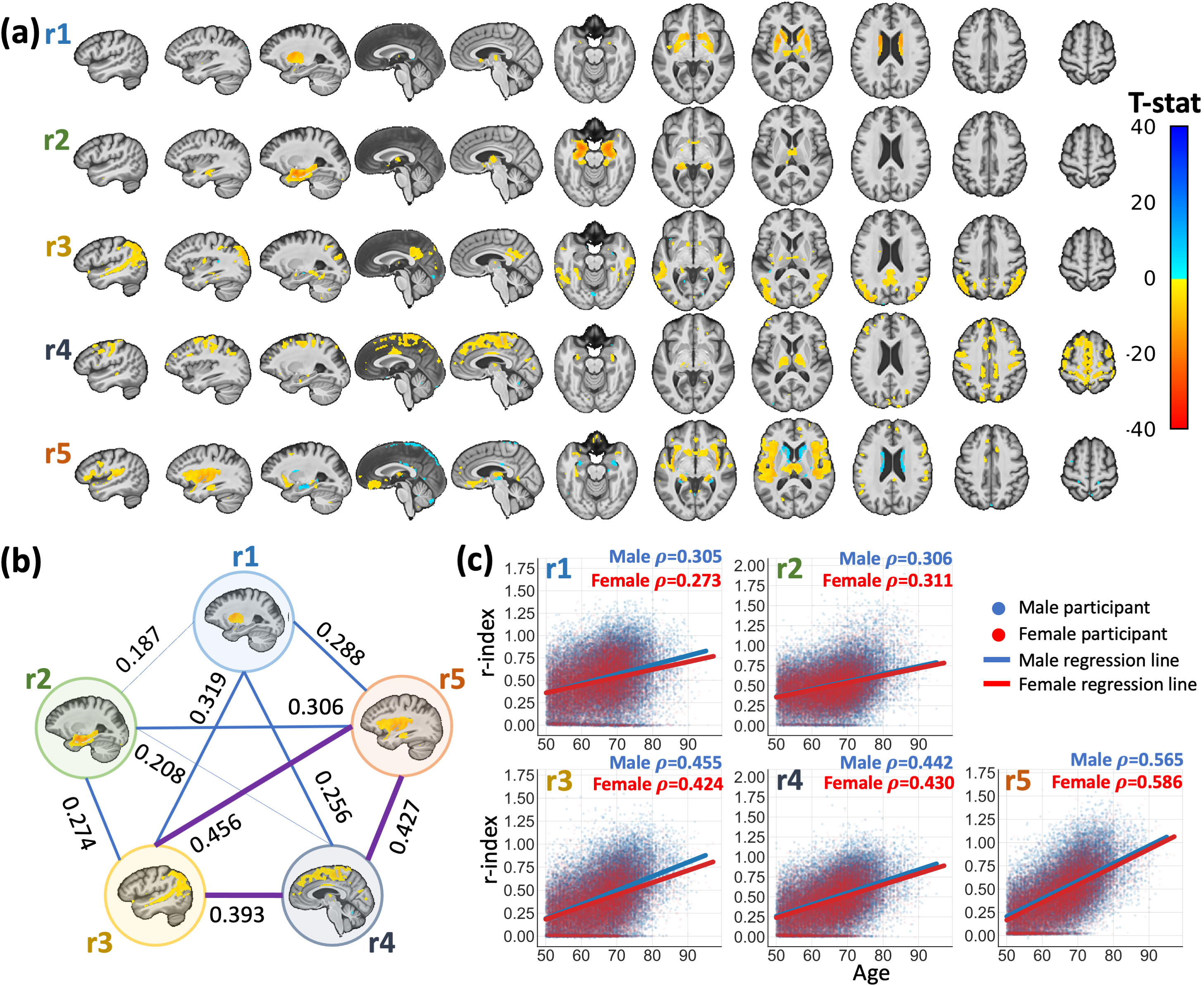
Surreal-GAN identifies five dimensions of brain atrophy of brain aging
Surreal-GAN quantify the severity of brain aging along five dimensions through the five r-indices (r1-r5), which revealed distinct patterns of associated brain atrophy. The five r-indices show correlations with each other while also exhibiting significant positive associations with chronological age. Additionally, expression of five dimensions at baseline not only show distinct associations with lifestyle factors, biomarkers, and chronic diseases, but also possess predictive values of future disease progression and mortality risk. For further details, refer to the work of Yang et al.
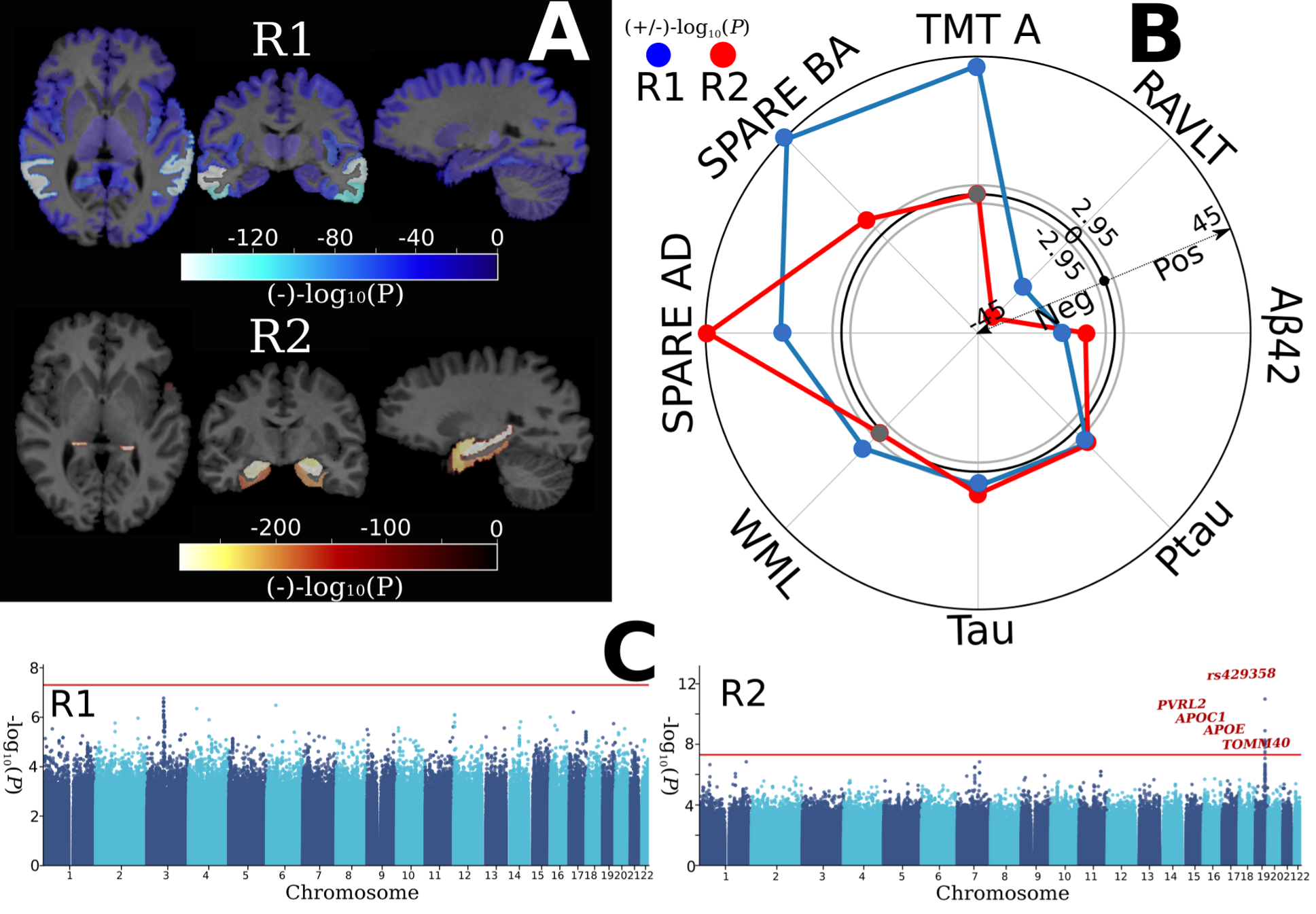
Surreal-gan identifies two dimensions of brain atrophy in MCI/AD population
Surreal-GAN identifies two distinct neuroanatomical dimensions, each reflecting the level of expression of a distinct pattern of brain atrophy. The two dimensions demonstrates distinct correlations with various clinical variables, biomarkers, and cognitive scores, including TMT-A, white matter lesion volumes, CSF Abeta, CSF Tau, etc. More significantly, expression of these two dimension were associated with genetic variants in both MCI/AD and general population. For further details, refer to the work of Wen et al.